Omnia Retail’s origin and purpose
In 2012, my co-founder and I had conversations with category managers from established online retailers in mature e-commerce categories, such as consumer electronics, and learned that they were spending a lot of time each week manually looking up prices of their competitors on comparison shopping engines and were still running behind with repricing the products in their assortment.
Propelled by e-commerce, product ranges were increasing in scope, and the heightened transparency of online pricing resulted in frequent price fluctuations. It became increasingly laborious and time-intensive to maintain competitive pricing as it required manual gathering of pricing data, calculation of optimal price points, and implementation of adjustments. This challenge led us to founding Omnia Retail.
Over the years, we saw that as other retail categories matured online, they struggled with the same problem. Similarly, over the last few years, brands have become more serious about their direct-to-consumer (D2C) channels. Brands selling a product against the initial Recommended Selling Price (RSP) for the whole product life cycle leads to insult pricing and the need to change their prices, yet again, to align with the market. As a result, we now see that brands are starting to struggle with the same problem that retailers experienced over a decade ago.
Simply being passionate about the challenge and using our prior retail and e-commerce knowledge, we applied our engineering expertise to solve this problem for retailers and brands. It was only later - when our company had grown to a size where everyone couldn’t fit on the same lunch table anymore - that we started reflecting on why we were so invested about solving this challenge. This very reflection led us to establishing Omnia’s purpose explicitly:
“We give retailers, brands and their teams superpowers by unleashing the full potential of pricing through market data, insights and automation.”
The most central concept here is the word “superpowers”. On a basic level, it refers to automating the tedious and time-intensive tasks that thousands of our users at retailers and brands had to manually do before: looking up prices of competitors, making calculations, and implementing changes. This already removes a lot of tedious work and frees up time to focus on more strategic and creative work. However, that is only one of the basic layers of “superpowers”.
Another more exciting element is that we enable our users to do things that were never possible before, even if they would have all the time in the world to spend on pricing. In terms of insights, an example is providing dashboards that provide our users with a “God-view” of the market: fully understanding their own price positioning and understanding what their key competitors (or resellers) are doing.
Regarding pricing automation, it’s about having nuanced and advanced strategies, understanding how they are set, impacting results in terms of price positioning and ultimately sales, and contribution margins.
Elements of success for dynamic pricing software implementations
Through the more than a decade of serving retailers and brands with pricing software, we have seen that certain elements lead to success and ensure the best returns on dynamic pricing implementations:
Clearly defined pricing objectives:
Begin by setting clear pricing objectives, emphasising the importance of starting with a clear end-goal in mind. Without clearly defined objectives one can have the greatest pricing platform in the world, but there is no guidance on how to use it, and how to measure success. It's essential to recognise that pricing objectives may vary across different parts and levels of the business and are likely to change in response to external factors. Therefore, the pricing platform must accommodate for these varying objectives to remain effective.
Securing engagement and support:
Securing the engagement and support of team members with direct involvement in pricing is crucial whether it’s as their core responsibility, such as dedicated pricing managers, or as part of their wider role like category managers and buyers. If these individuals struggle to implement the pricing strategies they aim for in the system, or if they cannot explain the prices suggested by the system, they may resist adopting the dynamic pricing software or, at the very least, lack the motivation to leverage the platform's potential fully.
Continuous improvement:
Rapid cycles of learning and enhancement drive ongoing improvement. This process is supported by ensuring all operations occur in the software's front-end. Any hardcoded rules established by a pricing software vendor in the back-end will hinder such a learning cycle. Moreover, maintaining transparency about the operational logic and performance metrics is essential.
From these elements of success we have learned at Omnia, we derived two essential design principles for developing our price management platform: flexibility and transparency.
Flexibility to remove barriers to adoption, improving results and ensuring control. Transparency to keep control while on auto-pilot, create buy-in from internal stakeholders and facilitate learning loops.
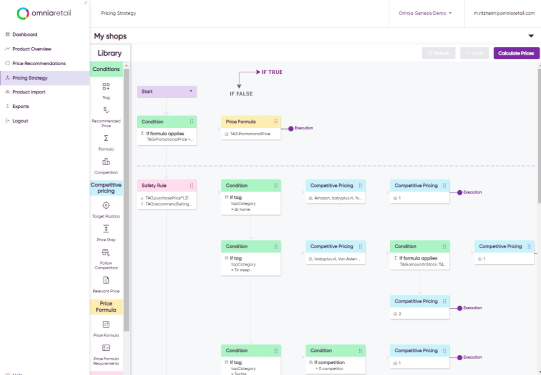
As the ability to run detailed and complex pricing strategies has become mainstream, it has created the next level of challenges: complexity overload. Omnia 2.0 successfully cuts through the clutter with its revolutionary visual pricing logic with the Pricing Strategy Tree™. It gives complete pricing flexibility and control, coupled with transparency.
The power of flexibility: Removing barriers to adoption, improving results and ensuring control
Flexibility is a core principle in our design philosophy, enabling our clients' users to execute any desired pricing strategy across all parts of their business. We have seen a vast array of pricing strategies being used and broadly speaking, they are driven by differences in objectives at the highest level, the need to differentiate on objectives on lower levels, and differences in definitions.
On the highest level, the main differentiation we see is between maximising revenues - with the constraint that a minimum contribution margin needs to be reached - and maximising contribution margin. Traditionally, we saw pure e-commerce players being primarily focused on the former, while more traditional omnichannel retailers were more focused on the latter. With the changing economy and higher interest rates, the importance of being profitable in the present, we now see pure e-commerce players also shifting more towards margin maximisation strategies.
While on the highest level, a retailer or brand might have a margin maximisation strategy, virtually, they will always need to differentiate on the lower level as well. Take for example a racket sports retailer. Although overall profit maximisation might be the main objective, the retailer might be focused on penetration (maximisation of sales, given a minimum margin constraint) in a market where they recently launched, as well as that being the main objective to establish itself in a nascent category like padel rackets.
Finally, we have learned that retailers and brands have differences of definitions and that their chosen software should support that, rather than enforcing a rigid rule or definition. Take the example of a stock-based strategy, where a company wants to automatically become more aggressive when stock coverage becomes too high or take the opportunity to steer toward margin when stock coverage becomes too low. The definitions of what’s too high and too low differ not only between companies, verticals and markets but also within a company and on different parts of its assortment.
It’s crucial for pricing software to be able to provide that flexibility and give the power to the user, not only to ensure that the retailer or brand can reach its objectives but also to ensure that there are no barriers in the adoption of the pricing software. If business users - like category managers - are not able to implement the strategies, they will be inclined to resist the implementation, putting the dynamic pricing implementation project at risk.
Pricing software must be able to support flexibility, but it’s even more crucial that everything is fully supported in the front-end of the user-interface (“the portal”). If there are rules or constraints hardcoded within the back-end, a common practice of some pricing software vendors in today's market, it leads to a lack of transparency and limits the pace of learning (testing with strategies). At Omnia, we’re proud to have this flexibility in our software, with not one line of customer-specific code while serving hundreds of retailers and brands since 2012.
The examples previously mentioned demonstrate how the principle of flexibility is integrated into the pricing automation part of the Omnia platform. However, our commitment to flexibility extends throughout the entire platform. For instance, we don't confine our customers to predetermined calculation schedules. Instead, they have full autonomy to set the timing for pricing data collection and dynamic pricing calculations. Additionally, they have the capability to initiate calculation runs manually at any moment from the front-end, such as when assessing the impact of strategy modifications. These calculations are efficiently completed within minutes, even for extensive product assortments.
Transparency to keep control while on auto-pilot, create buy-in from internal stakeholders and facilitate learning loops
Automation has the potential to save time and improve results. However, when implemented poorly, automation may lead to a lack of control. From the early years, this has been our belief, and preventing our dynamic pricing software from becoming a black-box has been a core design principle. Even in our earlier years, the Omnia software had a “Show me why™” button that took the user by the hand in terms of how the software arrived at a particular price advice.
Transparency in pricing software ensures control while being on auto-pilot. An element of this transparency is how your strategies will affect the prices for all products such as the number of products that received “price advice”: prices up, down, equal, price difference vs various benchmarks, and so on. One level deeper is the need for dynamic pricing users to understand the impact of every element of their pricing strategy. For example, one could have a very elaborate pricing strategy, but if anywhere in the strategy there would be a pricing rule “always adjust to the lowest price in the market”, there would be a high chance that the rule will set the prices for the majority of your assortment, and most likely down.
Understanding how elements of your strategy impact the eventual prices set links to another significant benefit of transparency: improving results by enabling learning loops. When implementing dynamic pricing you can achieve surprisingly strong results by implementing a pricing strategy once, and then never touching the system again. However, we see that customers who use our software more continuously and are evaluating and testing new approaches achieve the best results. This is only achievable with a pricing tool that creates maximum transparency, facilitating those learning loops.
The Pricing Strategy Tree™ as embodiment of flexibility and transparency
Our previous pricing platform, Omnia 1.0, was very flexible. However, our most advanced enterprise customers using complex pricing strategies could end up with a long list of pricing strategies. Although relatively easy to build up incrementally, this could make it hard to grasp the strategies running and the logic behind them.
In numerous instances, consultants specializing in pricing strategy assisted our customers by creating decision trees to map out and advise on their clients' strategies. This inspired us to use a decision tree as the main interface when building pricing strategies. Although we already had the idea of a Pricing Strategy Tree on our roadmap, acquiring German pricing strategy company Patagona GmbH at the end of 2021 gave us an unfair advantage. Patagona had developed a Pricing Decision Tree to build strategies in their Pricemonitor product. We evaluated this concept with our customers and based on their invaluable feedback, we developed the Pricing Strategy Tree as one of the core elements of our next-generation platform, Omnia 2.0. The new platform was launched in the Summer of 2023, with new product features being added monthly.

Not only does the Pricing Strategy Tree lead to more transparency in terms of letting our users understand what’s running, we see that in practice it also makes it easier and simpler to create strategies. That is because it’s a visual drag-and-drop interface, but also because we embedded functionality; such as copy-and-pasting of selected branches within the tree (typically set-up for one market or format) and copy-and-pasting of entire trees across countries or formats. The latter is particularly relevant for our global customers to be able to roll out pricing strategies to additional markets with just a few clicks.
To drive transparency even further, the Pricing Strategy Tree proved the ideal canvas for additional functionality: path tracking through the strategy tree, strategy branch statistics of the tree, and naming of tree branches. The path tracking is an evolution of the “Show Me Why™” in Omnia 1.0 called “Explain Price Recommendation” in the Omnia 2.0 platform and provides a full explanation of how the price advice of a particular product came about. This is a typical question for a business user as a category manager or buyer. The “Price Explanation” visually tracks the path through the tree to show the logic and how the price advice came about.

“Strategy Branch Statistics” covers another use case, one that was never possible in our previous Omna 1.0 platform: It highlights how elements of the overall pricing strategy impact the eventual prices set. It does this by showing how many products are repriced by each branch in the tree, the average price difference and percentage difference of the price advice vs current price points, as well as the number of products priced up and down.

One important benefit of this is that it gives our users insight into which branches are most dominant in setting the eventual prices. Remember the example of having an elaborate pricing strategy with a rule somewhere to “always adjust to the lowest price in the market” in the transparency section above. However, the value of Strategy Branch Statistics goes beyond that. It also provides users insights into the performance of a particular strategy branch, thereby facilitating the important learning loops discussed above.
Another functionality we have added to the Pricing Strategy Tree™ canvas is the naming of branches of the tree. Although the tree already makes it easy to show the logic applied, the naming of branches makes it even more practical for users and co-workers to understand what happens in a particular branch by describing it in natural language, for example “Follow the lowest price point of key competitors when stock coverage is too high”. The naming of tree branches also lays the foundation for the steps we plan to take providing more insights in the performance or effectiveness of branches.
|
“We have seen several pricing tools, but the pricing strategy tree plus “show me why” is a super unique selling point and best implementation of dynamic pricing we have seen so far.” |
AI is a means, not an end: A case for blending rules, AI, and goal-based pricing
We believe that AI as a powerful technology can greatly contribute to the “superpowers” in our purpose. Think about automated import mapping, creating reports based on natural language, surfacing conclusions from data and charts, and so forth. We are also convinced that AI will provide more and more value in the future core area of price setting. However, given the importance of transparency and flexibility, we firmly believe that the future of pricing setting won’t be AI only - on 100% of the products in 100% of the cases - but rather a combination of pricing rules and AI.
In terms of intelligence in price setting, AI is a means not an end itself. The core need that we see at the retailers and brands across our customer base is more focused on moving away from setting granular business rules - with the aim of reaching specific objectives - to rather focus on setting the objectives themselves at a higher level and letting our Omnia pricing platform optimise for that. As a company focused on and committed to delivering value to our customers, we naturally plan for this need with more and more goal-based “nodes” (blocks) in the Omnia Pricing Strategy Tree™.
Goal-based nodes can have a combination of complex AI running under the hood, for other goal-based nodes less complex statistical rules, depending on the need. The first example of such a goal-based node with AI under the hood is our Amazon Buy Box AI block whereby our user sets the Amazon Buy Box win probability certainty and the AI - based on large amounts of historical data - tries to land exactly at the right price point to reach maximum margin while keeping the win probability as a constraint. This is very different from the previous approach in our software and, to our knowledge, the current state of Buy Box optimisers in most channel management software which has usually been going step-by-step down until you win the Buy Box and then up again to increase margin. That approach is simply too slow and there are too many variables with influence that have changed in the meantime.

Although we envision that larger and larger parts of the assortment will be priced by such goal-based nodes in the future, we believe they will always be combined with business rules on part of the assortment (again, it will be rules and AI). For example, our users may want to apply hard constraints (such as upper and lower boundaries) which can differ on different parts of the assortment. For promotions, retailers and brands will want to set hard price points during a certain time frame. Those are just some examples of why the goal-based nodes need to be combined with business rules.
The crucial thing is that the principles of flexibility and transparency continue to be crucial when combining rules and AI. You need one single interface where rules and AI can be seamlessly combined, applied by business users, and it remains transparent how and why prices were set. Again, the Pricing Strategy Tree is the ideal concept that automatically ensures this. While this may seem to be a trivial design prerequisite, we see that other pricing software vendors that have begun making first steps with AI in their platforms often are violating this principle. There are vendors that offer “AI-only” with no capability to combine it with rules. We have seen vendors with a separate “AI-version” of their product, next to the old rule-based version of their product to let customers choose one of the products. Then, finally, there are vendors that perhaps are actually more of a team of pricing consultants, as they have to hardcode rules in the back-end, as well as requiring a lot of manual intervention from the team of the vendor for the algorithms to at least provide decent results. The latter case also leads to very long implementation times and learning loops that are too slow, as we learned when taking over customers of these vendors.
|
“With that pricing tree, the flexibility is almost endless.” |
Unleashing superpowers with Omnia 2.0
At Omnia, we believe we are still in the early stages of developing the ultimate pricing platform we aim for in the long term. Yet, we're immensely proud of how the Omnia 2.0 platform is already giving our customers superpowers by enhancing their capabilities more and more. We have made huge leaps in terms of dashboarding, and are constantly evolving those dashboards on a weekly basis thanks to the great feedback from our customers, and the way we have decoupled the visualisation layer from the data layer, enabling us to make fast interactions with little development time. We are clearly on the path of having that “God-view” of the market from the introduction above.
Perhaps an even bigger leap has been the core topic of this article: the introduction of the Pricing Strategy Tree in Omnia 2.0, which combines ultimate flexibility and transparency, and we believe is the ideal concept to combine business rules with (partially AI-driven) goal-based pricing.
We couldn’t be more proud of the feedback we have received from our customers, and the market as a whole, since the launch of Omnia 2.0 in the Summer of 2023. And we are very excited about further growing the superpower of our users by adding more intelligence to the Pricing Strategy Tree and the entire Omnia 2.0 pricing platform.


.png?height=766&name=ORA%20Visuals%2020252026%20(11).png)